What is an Automotive Fuse?
An automotive fuse is an electrical component that is designed to protect other components, devices, and wiring from any damage that might occur due to excess current flow. Most automotive fuses are designed for 12v electrical systems, so they are primarily identified by an amperage rating. This rating refers to the maximum amount of amperage that the fuse can handle before it fails. Automotive fuses are typically contained within fuse boxes, but some applications also use inline fuses.
Contents
Types of Automotive Fuses
There are five primary types of automotive fuses:
- Blade
- Bosch
- Glass tube
- Limiter
- Lucas
Some of these types of fuses are in widespread use, and others are primarily found in older vehicles. Bosch type fuses and glass tube fuses, for example, are mainly found in old European and American vehicles, respectively.
In addition to these types of fuses, a related component called a fusible link is sometimes used in automotive applications. Fusible links perform essentially the same function as fuses, but they are used exclusively in high current applications to components like the generator, alternator, or starter.
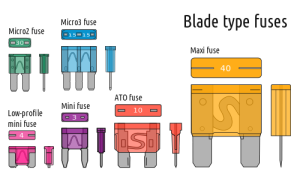
Blade Type Automotive Fuses
Blade type fuses were developed in the late 1970s, and they have been widely used in automotive applications since the 1980s. Unlike other fuse types, there are several different sizes of blade fuses:
- Micro2
- Micro3
- Low-profile mini (APS, ATT)
- Mini (APM, ATM)
- Regular (APR, ATC, ATO)
- Maxi (APX)
All of these blade fuses share the same basic design, which consists of two metal blades that are encased in a thin, rectangular piece of semi-translucent plastic. The blades are connected by a third piece of metal that is thinner than either blade. This center piece of metal is the part of the fuse that is designed to fail when a specific level of current flows through it. When that happens, this thin strip will break electrical contact between the two blades.

In some cases, it can be difficult to tell if a blade type fuse is blown. This fuse looks good, but it isn’t.
These fuses are relatively easy to remove and replace, although a special fuse puller tool is often included inside automotive fuse boxes.
Glass Tube Fuses
Prior to 1981, American cars typically used glass tube fuses. These fuses consist of two metal end caps with a glass tube between them. Inside the tube, and connected to the end caps, a thin wire or metal strip provides electrical contact. This wire or strip is designed to fail when a specific level of current flows through it.
Glass tube fuse specifications are defined in SAE J554. These fuses are all 1/4 inch in diameter, but they can vary in length depending on the amperage rating. The type of wire or strip inside the tube also varies depending on that rating.
Although glass tube fuses are no longer used in modern automotive applications, they are still available for older vehicles.
Bosch Type Fuses
Bosch type fuses are roughly cylindrical in shape like glass tube fuses, but they are made primarily out of plastic or ceramic materials. Unlike glass tube fuses, the metal end caps of these fuses have pointed ends. That led to Bosh type fuses being referred to as torpedoes.
These fuses were primarily used in older European automobile applications like BMW. They are still available for use in those older applications, but glass tube fuses with conical ends have also been developed as an alternative.
Automotive Fuse Color Coding
Some types of automotive fuses use color coding to indicate the current rating. Blade, Bosch, and Lucas type fuses all use their own systems. This allows the amperage rating to be determined at a glance if the printed number can’t be read. However, the color coding systems are not the same across different types of fuses. Even within different sizes of blade type fuses, the Maxi style doesn’t conform 100 percent to the same coding that regular, mini, and low-profile mini fuses use.
Automotive Fuse Failure
An automotive fuse can fail due to age or due to an issue in the circuit that it is designed to protect. As long as the same amperage rating fuse is used, it is typically safe to simply replace a blown fuse with a new one. If there is an issue in the circuit, the fuse will simply blow again.
Although it is often possible to tell if a fuse is blown by looking at it, some fuses can fail in such a way that they appear to still be connected. That’s why it’s always a good idea to check for a blown fuse with a test light. By checking for power on each fuse, it is possible to determine whether any of them are broken.